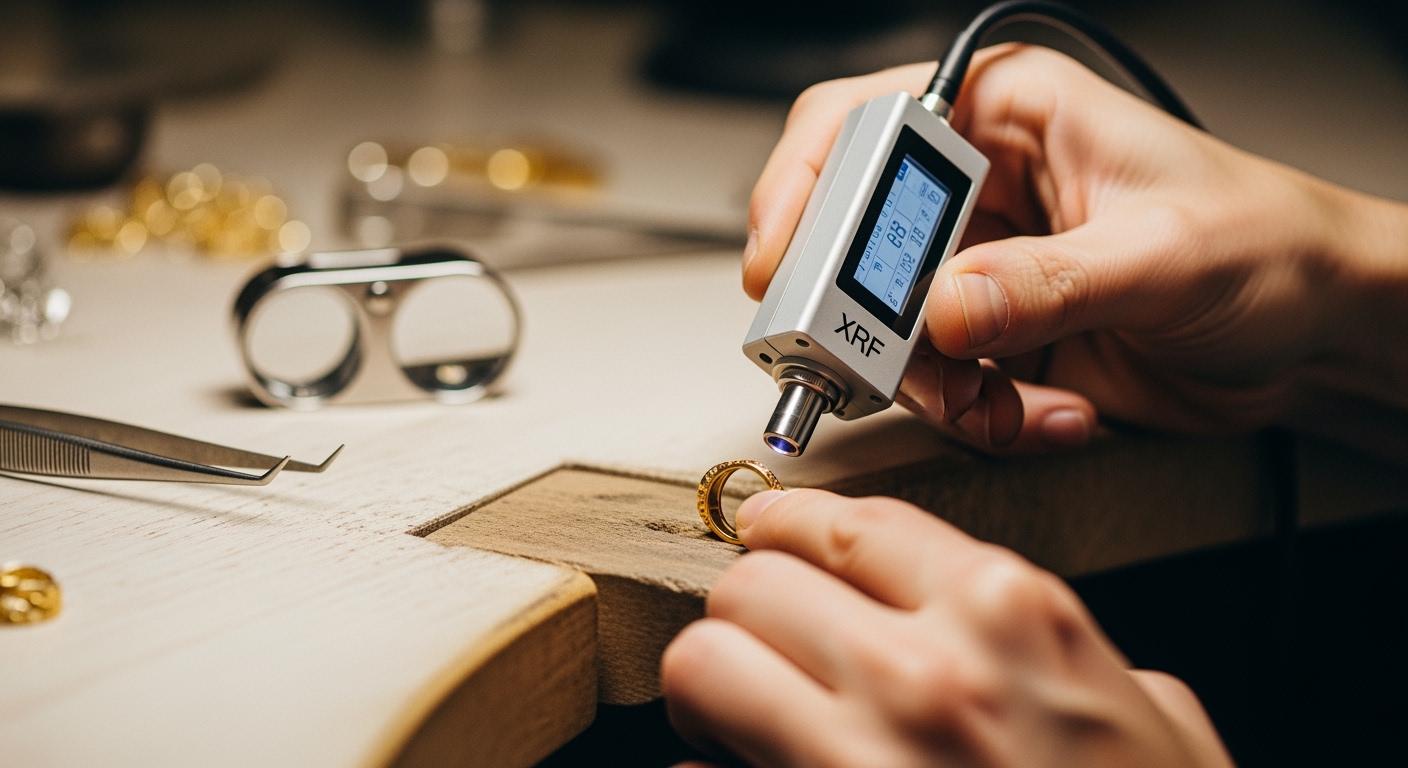
In the high-stakes world of precious metal trading and jewelry manufacturing, the ability to accurately verify purity is the cornerstone of business integrity. Traditional methods, such as manual acid testing or destructive fire assay, often fall short of modern standards—either by damaging the specimen or providing subjective results. This is where X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) technology has revolutionized the industry.
XRF technology provides jewelers with a sophisticated, non-destructive analytical technique for identifying the complete elemental profile of gold, silver, platinum, and other alloys. By utilizing high-energy X-rays to trigger atomic-level emissions, professional XRF gold analyzers deliver precise results in seconds, achieving accuracy levels comparable to traditional laboratory assays with relative standard deviations often below 0.2%. This guide explores the technical mechanics, hardware variations, and operational benefits of integrating XRF into your jewelry business.
Key Takeaways
Non-Destructive Integrity: Analyze high-value assets without scratches, chemical exposure, or heat, preserving the item’s condition.
Atomic Level Accuracy: Spectroscopic analysis provides a 99.9% accurate breakdown of Gold, Silver, Platinum, and hazardous trace metals.
Rapid Throughput: Generate detailed digital reports in under 10 seconds, facilitating fast transactions and efficient inventory management.
Advanced Fraud Protection: Instantly detect tungsten-filled bullion or heavy-plated simulations that bypass density and weight tests.
Professional Credibility: Utilizing modern instrumentation builds unshakeable trust with retail and wholesale clients.
The Physics of Elemental Fingerprinting
X-ray Fluorescence, or XRF, is a branch of emission spectroscopy. It operates on the principle that every element has a unique “atomic fingerprint” defined by its electron configuration. When a sample is irradiated with a primary X-ray beam from a high-voltage tube, it displaces electrons from the inner orbital shells (K or L shells) of the atoms.
To regain stability, electrons from higher-energy outer shells drop down to fill these vacancies. During this transition, they emit secondary X-rays (fluorescence) with an energy characteristic of that specific element. A high-resolution detector within the spectrometer captures these photons, and the software processes the energy-dispersive data (EDXRF) to calculate the exact percentage of each metal in the sample.
Hardware Matters: SDD vs. Si-PIN Detectors
For jewelers, the choice of detector is the most critical hardware decision. Modern XRF spectrometers typically use one of two types:
Si-PIN Detectors: A cost-effective, durable option suitable for general karat verification. It is ideal for shops that need basic screening for 10K to 24K gold.
SDD (Silicon Drift Detectors): The premium standard. SDD technology offers higher count rates and better spectral resolution, allowing the device to distinguish between elements with close atomic numbers and detect trace impurities with 10x higher sensitivity.
Technological Advantage | Impact on Jewelry Valuation |
|---|---|
Matrix Correction (FP Method) | Corrects for “inter-element effects” to ensure 18K white gold is read accurately despite nickel interference. |
Spectral Resolution | Separates the signal of gold from surrounding silver or copper with extreme precision. |
Digital Traceability | Generates printable certificates that provide a “digital assay” for every customer transaction. |
Hazardous Element Detection | Identifies prohibited trace metals like Cadmium (Cd) or Lead (Pb) to ensure regulatory compliance. |
Practical Implementation in the Jewelry Workflow
Integrating XRF technology into a daily workflow requires an understanding of sample preparation and instrument selection. Unlike wet chemistry, XRF is nearly instant, but accuracy depends on standardized protocols.
The Step-by-Step Analysis Protocol
Sample Sanitization: Wipe the jewelry surface with alcohol to remove fingerprints or oils, which can cause minor spectral attenuation.
Target Alignment: Place the item in the analysis chamber. High-end benchtop models feature internal cameras to focus the X-ray spot precisely on the metal band rather than the gemstones.
Excitation Phase: The X-ray tube activates, bombarding the sample with high-intensity photons. This phase usually lasts between 5 and 30 seconds depending on the required precision.
Data Interpretation: The instrument’s software utilizes Fundamental Parameter (FP) algorithms to compare the fluorescent energy against known standards, providing a complete karat reading and metal breakdown.
Classifying XRF Instruments for Jewelry
Jewelers must choose between benchtop and portable platforms based on their specific business model. A retail jeweler on a showroom floor has different requirements than a mobile appraiser or a precious metal refinery.
Platform Type | Recommended Use | Accuracy Level |
|---|---|---|
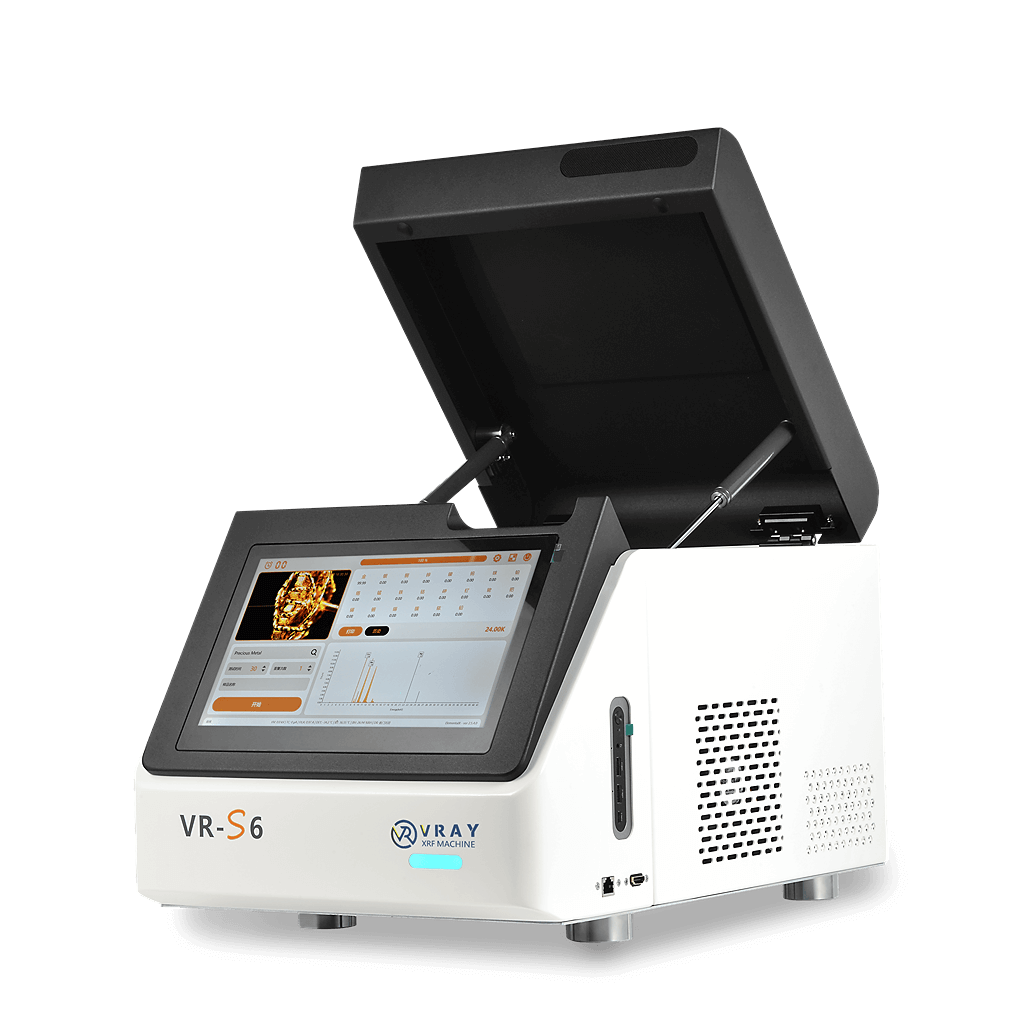
Benchtop XRF Analyzer | Quality control, showrooms, and refining laboratories. | Highest (Precise up to 0.01%) |
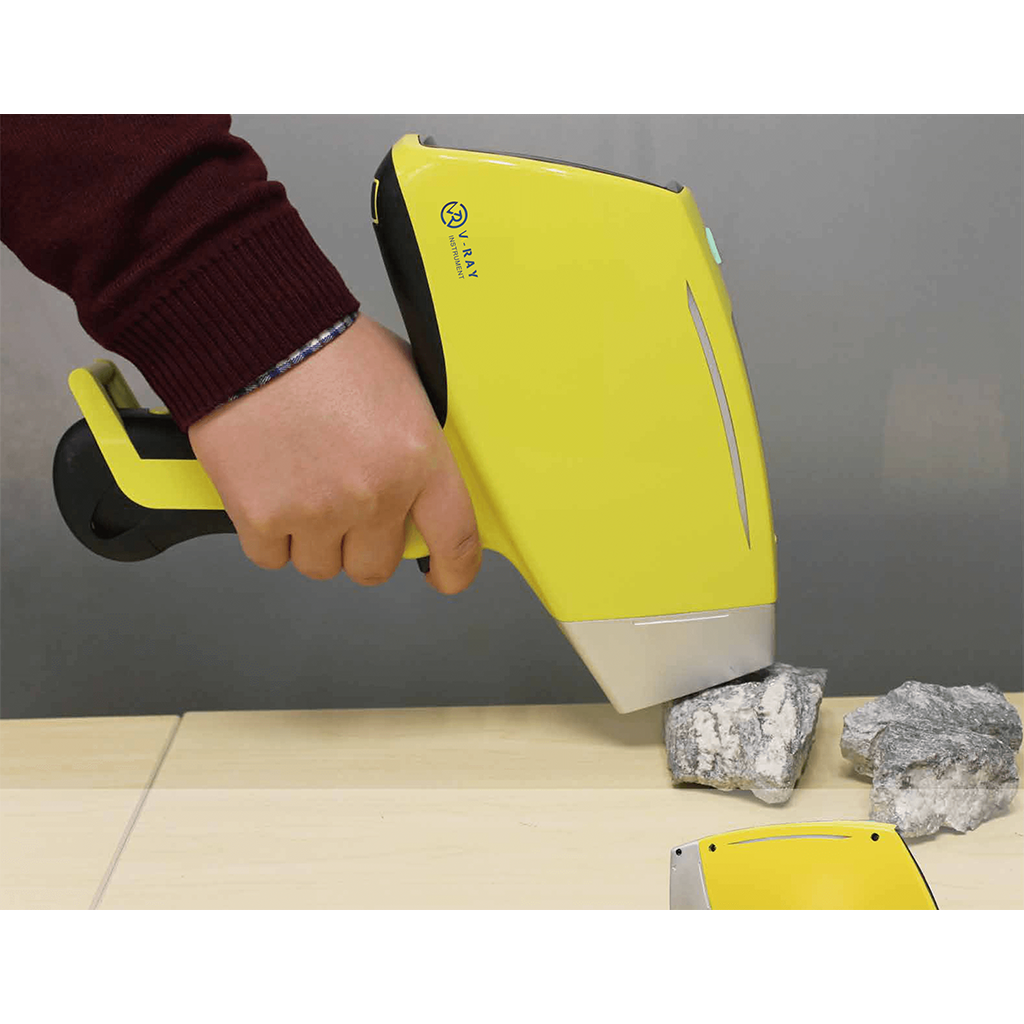
Portable/Handheld XRF | On-site scrap buying, field exploration, and pawn intake. | High (Precise up to 0.1%) |
Integrated In-Line XRF | Large-scale industrial manufacturing and recycling. | High (Continuous monitoring) |
Professional Note: A benchtop unit generally offers better shielding and a larger detection area, while portable XRF analyzers offer unmatched flexibility for field appraisals.
Detecting “Smart Fakes” and Plating Discrepancies
One of the most valuable applications of X-ray fluorescence is the detection of sophisticated counterfeits. “Smart Fakes”—items like tungsten-filled bars—are engineered to match gold’s density exactly, making them invisible to traditional scales and water displacement tests.
Coating Thickness and Material Verification
Advanced XRF software can perform “Positive Material Identification” (PMI). Because X-rays can penetrate several microns into a surface, the analyzer can detect if the silver or gold signal drops off rapidly, indicating a heavy electroplate (HGE) or gold-filled shell. This coating thickness analysis is vital for determining the true value of scrap gold lots and preventing the acquisition of low-value simulants at solid gold prices.
Gold Type | XRF Detection Logic | Jewelry Application |
|---|---|---|
Gold Flash | Detects base metal immediately beneath < 0.25µm shell. | Budget costume jewelry. |
Gold Vermeil | Identifies 2.5µm gold layer over a Sterling Silver signal. | Premium plated silver. |
Solid 18K Gold | Detects consistent 75% Au / 25% Alloy ratio. | Fine luxury jewelry. |
Economic ROI: The Business Case for XRF
While the initial investment in a quality XRF analyzer may seem substantial, the Return on Investment (ROI) is often measured in months. By eliminating “melt loss”—where a refinery pays for more gold than is actually present—and avoiding the purchase of a single high-value counterfeit bar, the device pays for itself. Furthermore, the speed of testing allows a shop to process 10x more transactions per day than a technician using chemical scratch tests.
Future-Proof Your Business: Don’t leave your reputation to chance. Explore VRAY’s range of professional gold analysis solutions and elevate your appraisal standards today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does XRF testing differ from acid testing?
XRF testing uses X-rays to analyze the atomic composition of a metal without causing any physical or chemical change. Acid testing requires scratching the item and applying corrosive chemicals, which is destructive and only provides a surface-level estimate of purity.
Can XRF detect fake gold inside a thick bar?
XRF is a surface and near-surface technique. It can detect plating and verify the alloy composition of the outer shell. For massive bullion bars, XRF is often paired with ultrasonic testing to ensure the core is not filled with tungsten or lead.
Is XRF analysis safe for gemstones?
Yes. Modern XRF analyzers use low-energy X-ray beams that do not interact with the crystal lattice of most common gemstones like diamonds, sapphires, and rubies. It is a completely safe, non-contact method for finished jewelry.
Does XRF require special training?
While basic operation is as simple as “point and shoot,” professional results require an understanding of sample cleaning and target alignment. Most VRAY Instrument packages include simplified software interfaces designed specifically for non-technical retail staff.
Can XRF distinguish between white gold and platinum?
Instantly. Because platinum (Pt) and gold (Au) have vastly different atomic weights and energy signatures, the spectrometer can differentiate them in less than 2 seconds, even if the white gold is rhodium-plated.