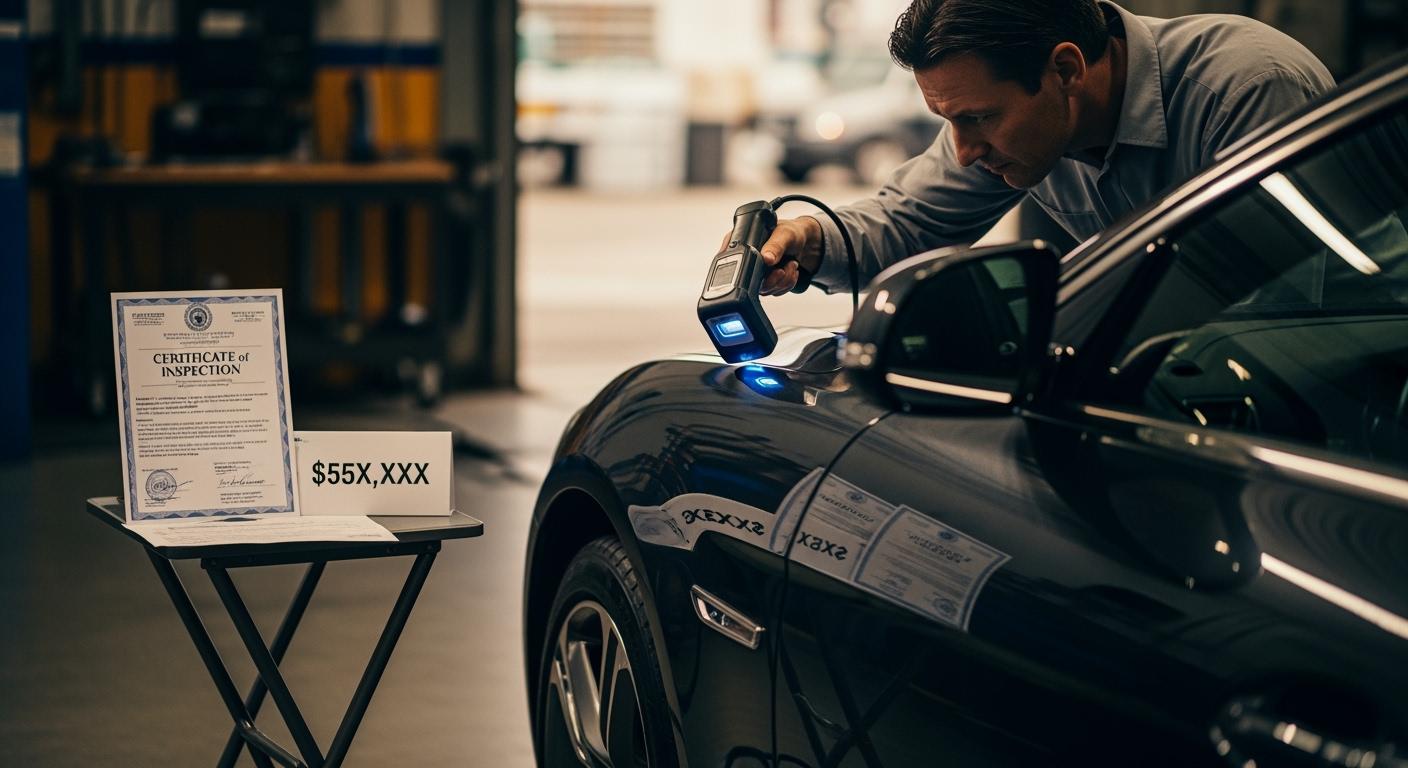
In the global secondary market, the difference between an asset’s “asking price” and its “closing price” often hinges on a single factor: verifiable condition. For high-value commodities ranging from precision-engineered jewelry to aerospace components, the ability to prove metallurgical purity or structural integrity without compromising the item is a transformative economic advantage. This is the domain of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)—a suite of analytical methodologies designed to “see through” materials without inflicting even a microscopic degree of damage.
Whether you are a retail jewelry buyer, a pawnbroker, or an industrial fleet manager, NDT represents a permanent insurance policy for your capital. By utilizing advanced XRF spectroscopic analyzers and other non-invasive evaluative tools, businesses can provide doubt-free assurance to potential buyers, thereby maximizing the intrinsic and market value of every asset. This guide explores the science of NDT and its profound impact on the economics of resale.
Key Takeaways
Asset Condition Retention: NDT allows for qualitative and quantitative analysis while keeping the specimen in “factory-new” condition.
Scientific Transparency: Utilizing atomic-level analysis (like XRF) eliminates the “trust gap” in high-value transactions.
Defect Preemption: Identifying subsurface cracks or alloy discrepancies early prevents catastrophic failure and preserves marketability.
Resale Premium: Assets backed by a digital NDT report typically command a 15-25% price premium in the secondary market.
Safety & Compliance: In regulated industries, non-destructive validation is often a legal prerequisite for transfer of ownership.
The Technical Landscape of Non-Destructive Evaluation
Non-Destructive Testing is not a single tool but a comprehensive technical framework. The choice of methodology depends on the material type, the expected defect profile, and the depth of penetration required. For most high-value assets, the goal is “Volumetric Integrity”—knowing that the core of the material is as sound as the surface.
Core Methodologies in Professional NDT
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF): The industry standard for precious metals and alloy identification. It utilizes the photoelectric effect to excite atoms, measuring the resulting fluorescent energy to create a metallurgical “fingerprint.”
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect subsurface voids. It is the primary tool for identifying tungsten cores inside solid gold bullion.
Radiographic Testing (RT): Employs X-rays or gamma rays to produce internal imaging of complex assemblies, vital for aerospace and heavy machinery.
Eddy Current Testing (ECT): Uses electromagnetic induction to detect surface and near-surface cracks in conductive materials like aluminum and titanium.
NDT Principle | Physical Mechanism | Ideal Application | Penetration Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
XRF Analysis | Atomic Shell Excitation | Jewelry, Scrap Metal, Ores | Surface/Near-Surface |
Ultrasonic | Acoustic Impedance | Bullion Bars, Welds, Pipes | Deep Volumetric |
Radiography | Photon Absorption | Aerospace Parts, Castings | Full Assembly |
Magnetic Particle | Flux Leakage | Ferromagnetic Engines | Surface Only |
The Economic Divergence: NDT vs. Destructive Testing
Historically, verifying an item’s composition meant “sacrificing” a portion of it. For a jeweler, this meant fire assay (melting a portion of the ring) or acid scratching. For an industrial engineer, it meant tensile strength testing to failure. While these methods are accurate, they are economically catastrophic for the resale market. NDT stands apart by providing the same level of scientific certainty without devaluing the asset.
When an asset is damaged for testing, its status shifts from “Finished Good” to “Refined Scrap.” This transition can result in a 30% to 70% loss in retail value. In contrast, non-destructive evaluation preserves the aesthetic finish and structural integrity, ensuring the asset remains market-ready immediately after the test.
Maximizing the Resale Value of Precious Metals
In the jewelry and bullion sectors, NDT has revolutionized procurement and sales. As counterfeiters develop “Smart Fakes”—base metals that mimic gold’s density—visual hallmarks are no longer sufficient. High-precision XRF spectrometers allow sellers to demonstrate the exact karatage (down to 0.01% precision) to a buyer in real-time.
Building the “Certificate of Trust”
A jewelry piece with a digital assay report from a VRAY spectrometer is exponentially easier to sell than one backed only by a verbal promise. This digital footprint acts as a “Carfax for Jewelry,” documenting that the item has been verified as non-plated, non-hazardous, and metallurgically authentic. As the NDT market expands toward a projected $6.2 billion by 2030, this level of documentation will become the standard requirement for all luxury transactions.
“Destruction is the enemy of value. In the modern appraisal market, if you can’t test it without marking it, you’re not valuing it—you’re destroying its history.”
Industrial Applications: Aviation, Automotive, and Beyond
For high-performance assets, NDT is a safety mandate that doubles as a value preserver. In aviation, the maintenance records of an aircraft (including ultrasonic scans of the turbine blades) are often worth as much as the hardware itself. A single “NDT-certified” engine component holds a significantly higher resale price than a “serviceable” part without documented non-destructive validation.
Regular NDT inspections detect microscopic fatigue cracks that, if caught early, can be repaired. If left undetected, they result in the total loss of the asset. This proactive integrity management ensures that the machinery remains at peak performance throughout its operational life, securing its eventual resale price.
Industry Sector | NDT Utilization | Impact on Liquidity |
|---|---|---|
Pawn & Jewelry | XRF Alloy Verification | Instant cash-out at fair market rates. |
Oil & Gas | Condenser/Pipe Inspections | Reduces downtime and secures safety audits. |
Automotive | Weld & Frame Integrity | Guarantees safety standards for used vehicles. |
精錬所 | Melt Analysis | Prevents procurement of contaminated scrap. |
Overcoming Implementation Barriers
Despite the overwhelming benefits, some businesses hesitate to adopt NDT due to perceived costs. While high-precision XRF analyzers represent a capital expenditure, the ROI (Return on Investment) is measured in the prevention of fraud and the preservation of asset status. For small operations, partnering with certified third-party testing labs provides access to these technologies without the initial equipment cost.
Professional Advice: When purchasing used industrial equipment or high-value jewelry, always ask for the “NDT Log.” An asset without a history of non-destructive verification should be valued with a significant risk discount.
The Future of NDT: AI and Automation
The next frontier of NDT is the integration of Artificial Intelligence. Automated XRF sorting and AI-driven crack detection algorithms are removing the potential for human error in evaluation. This “Machine Learning Integrity” provides a level of consistency that further boosts buyer confidence. For the转售 market, this means that an evaluation conducted in New York will match an evaluation conducted in Tokyo, creating a truly globalized and liquid market for verified assets.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does XRF testing protect the finish of a ring?
XRF utilizes a low-energy X-ray beam that interacts only with the electrons of the metal atoms. It does not generate heat, mechanical friction, or chemical reactions. Once the test is finished, the ring is physically and chemically identical to its pre-test state.
Can NDT identify “heavy plating” in scrap gold?
Yes. Advanced non-destructive analyzers can detect the spectral attenuation that occurs when gold is layered over a base metal. By analyzing the intensity ratios of secondary X-rays, the device can flag if a piece is solid or just a surface-treated simulant.
Is NDT required by law for certain resales?
In industries like aviation and nuclear power, regular NDT inspections are strictly mandated by regulatory bodies like the FAA or IAEA. In the jewelry market, it is not currently a law, but it has become a “de facto” standard for reputable dealers.
Why is destructive testing still used at all?
Destructive testing is used in the manufacturing design phase to determine the “Ultimate Tensile Strength” or failure limits of a new material. However, for individual asset valuation and resale, non-destructive methods are the only logical choice.
How often should high-value assets undergo NDT?
For jewelry, an XRF check should be performed at every point of sale. For industrial machinery, the frequency is determined by “Cycle Count” or “Flight Hours,” as specified in the manufacturer’s maintenance manual.