
Today’s gold prices shift mainly due to changes in the US dollar, real interest rates, and investor demand from both ETFs and central banks. Le gold industry and gold analysis show that central banks have increased their reserves, especially during global tensions. Investors rely on gold investment as a safe haven when uncertainty rises. The gold industry adapts quickly to these shifts, making it important for investors to watch these factors closely.
Principaux points à retenir
Gold prices mainly change due to real interest rates, the US dollar value, inflation, geopolitical risks, and central bank actions.
When real interest rates fall or turn negative, gold becomes more attractive because it holds value better than low-yield savings.
Gold prices often rise when the US dollar weakens, but strong geopolitical tensions can push gold prices up even if the dollar is strong.
Investors buy gold to protect their wealth during inflation and uncertain times, making gold a trusted safe-haven asset.
Central banks and investors buying gold support higher prices, so watching their actions helps predict gold price movements.
Key Factors Influencing Gold Price

Understanding the key factors influencing gold price helps investors make better decisions. Each factor affects gold prices in different ways, often working together to shape the market.
Real Interest Rates
Real interest rates show how much money grows after removing inflation. When real interest rates fall or turn negative, gold becomes more attractive. This happens because gold does not pay interest, so when savings accounts or bonds offer little or no real return, people look for other options. Gold acts as a store of value, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
Gold prices often rise when real interest rates drop below zero. Par exemple, between 2008 et 2012, and again from 2019 À 2021, negative real yields led to strong gold price rallies. Historical data shows a negative correlation between real interest rates and the price of gold, with a 1% increase in real rates lowering gold prices by about 13.1%.
Period/Event | Interest Rate Movement | Gold Price Movement | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Rising inflation and interest rates | Gold rose from ~$100 to $850 per ounce | Gold soared despite rising rates due to high inflation | |
2006 (Bank of England hike) | Rate hike from 4.75% À 5.25% | Gold prices declined | Shows direct influence of monetary policy |
2008 financial crisis | Falling/negative real rates | Gold prices surged | Gold acted as a safe-haven asset |
Gold’s role as a safe-haven asset becomes even stronger during times of negative real interest rates and economic downturns.
US Dollar Value
The value of gold often moves in the opposite direction of the US dollar. When the dollar weakens, gold prices usually rise, and when the dollar strengthens, gold prices often fall. This happens because gold is priced in dollars worldwide. If the dollar loses value, it takes more dollars to buy the same amount of gold.
The US dollar is currently 10-15% overvalued compared to its fair value.
Gold price increased from about $2,160.80 one year ago to nearly $2,978 in mid-2025, a 37.82% rise.
Sometimes, both gold and the dollar rise together during periods of financial instability, as investors seek safe-haven assets.
Recent trends show that central bank gold purchases and geopolitical factors can push gold prices higher, even when the dollar is strong. Investors should watch both the dollar and other key factors to understand gold price movements.
Inflation Trends
Inflation means prices for goods and services are rising. Many people buy gold to protect their wealth from losing value during inflation. Gold is seen as a store of value and a safe-haven asset during periods of high inflation and inflation concerns.
Statistical Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
Cointegration Tests | Gold prices show a strong relationship with money supply, but not always with CPI inflation. |
Regression Analysis | Gold returns do not always move directly with inflation, except when inflation expectations change. |
Historical Patterns | Gold prices fell during the mid-2010s despite rising inflation, but surged during COVID-19 and 2023 inflation spikes. |
Inflation-adjusted gold prices show that gold does not always move in line with inflation. Other factors, like investor sentiment and monetary policy, also play a role. Par exemple, in June 2022, US inflation reached 9.1%, and gold prices remained stable, reinforcing gold’s reputation as a safe-haven asset.
Geopolitical Uncertainty
Geopolitical factors, such as wars, conflicts, and political tensions, have a strong impact on the price of gold. During times of geopolitical and economic uncertainty, investors often buy gold as a safe-haven asset. Gold prices tend to rise quickly when global risks increase.
Studies show that gold acts as a hedge against geopolitical risk and economic uncertainty.
Gold prices respond rapidly to uncertainty shocks, often within one month.
Major events, comme le 2024 Middle East tensions, pushed gold prices near all-time highs.
Gold’s role as a safe-haven asset is clear during periods of crisis. Investors around the world turn to gold to protect their wealth when geopolitical factors create instability.
Central Bank Actions
Central banks play a major role in the gold market. Their actions can influence both the supply and demand for gold. When central banks buy gold, they support higher prices and set a price floor. When they sell, they can add to supply and put downward pressure on prices.
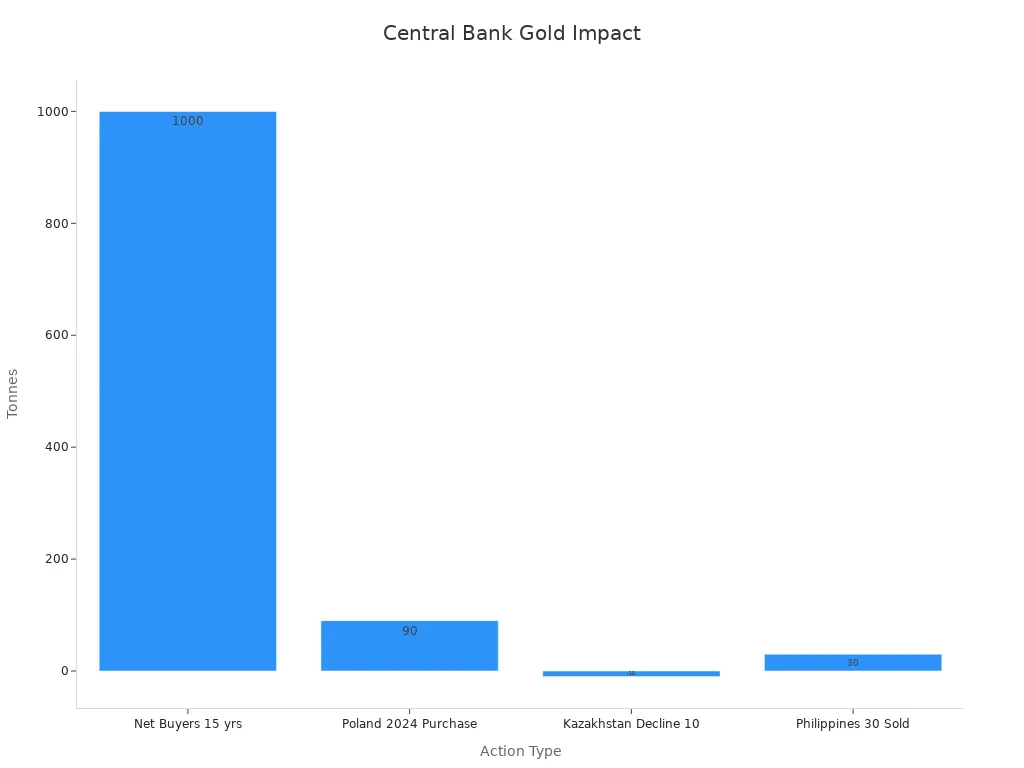
Central banks have been net buyers of gold for 15 années, purchasing over 1,000 tonnes annually from 2022 À 2024.
Developed market central banks hold about 28.3% of their reserves in gold, while emerging markets hold 13.1%.
Some central banks, like Poland and Kazakhstan, adjust their gold holdings to manage inflation or liquidity.
Central bank actions are sometimes hidden or delayed in official reports, making their true impact on gold prices hard to measure. Toutefois, their steady demand supports the value of gold and reinforces its role as a safe-haven asset and store of value.
Demand for Gold and Supply Trends

Investment Demand
Investment demand plays a major role in shaping gold prices. Investors buy gold through exchange-traded funds (ETFs), Bars, and coins, especially during times of economic uncertainty. In Q3 2024, ETF inflows doubled year-over-year, reaching 95 tonnes. Central banks also increased their gold holdings, signaling strong support for higher prices. When investment demand rises, gold prices often climb. Market research shows that falling interest rates, geopolitical risks, and the need for portfolio diversification drive more people toward gold investment. The table below highlights recent trends:
Metric | 2023 Valeur | 2024 Valeur | Q4 2024 Valeur |
|---|---|---|---|
Annual Investment (tonnes) | N/A | 1,180 (+25%) | N/A |
ETF inflows (tonnes) | N/A | 364 | 95 |
LBMA Gold Price (US$/oz) | 1,940.5 | 2,386.2 (+23%) | 2,663.4 |
Consumer and Cultural Demand
Consumer and cultural demand for gold shapes the market in unique ways. In many Asian countries, gold holds deep cultural value. People in China and India buy gold jewelry for weddings, festivals, and as gifts. Studies show that Hong Kong’s per capita gold consumption is 14 times higher than in the United States. Even when incomes are lower, cultural traditions keep demand for gold strong. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Western countries saw increased demand, while some Asian and Middle Eastern countries experienced a drop. These patterns show how culture and tradition can influence gold prices and demand for gold across the world.
Mining and Recycling Supply
Gold supply comes mainly from mining and recycling. About 74% of gold supply comes from mining, while 23% comes from recycled scrap, et 3% from electronic waste. In the first half of 2024, mine production reached an all-time high, and recycling volumes hit their highest level since 2012. The chart below shows recent changes in gold supply:
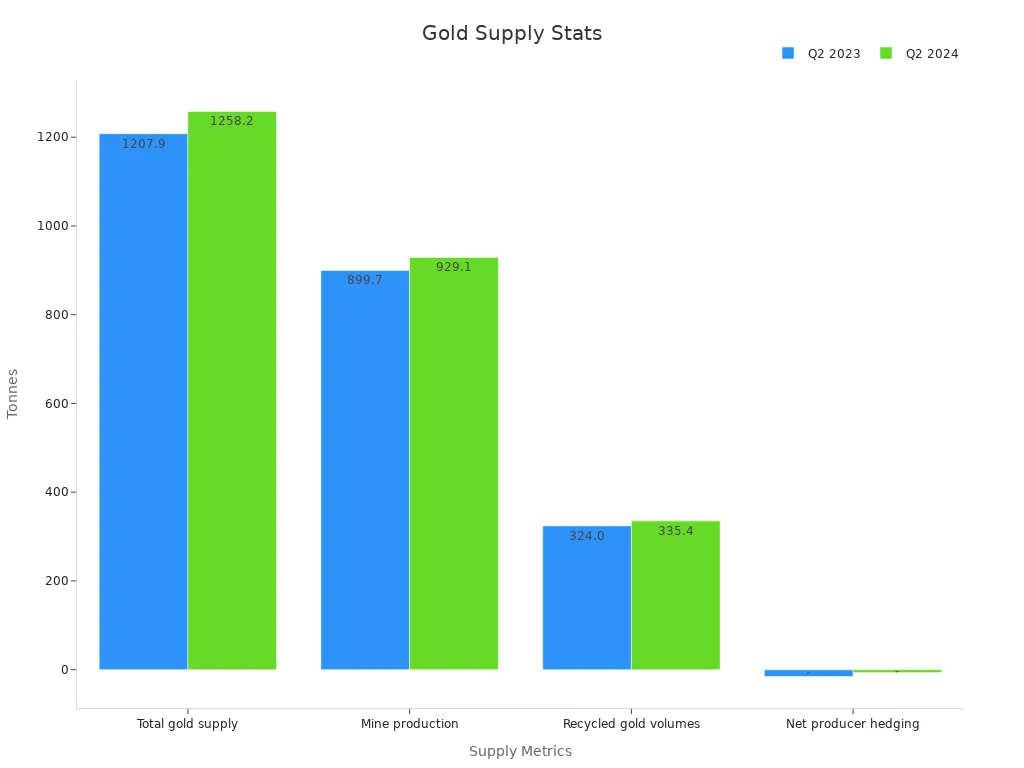
When gold prices rise, recycling activity increases, especially in regions like Europe and China. Supply and demand work together to set gold prices. If gold supply cannot keep up with rising demand for gold, prices usually go up.
Gold Industry and Gold Analysis
Macroeconomic Factors
Le gold industry and gold analysis show that economic factors play a major role in shaping gold prices. Inflation, unemployment, and consumer confidence all influence how investors view gold. Recent research finds that gold tends to rise by about 1.5% for every 1% increase in inflation. Changes in global economic factors, such as Gross Global Product and oil prices, also affect the gold industry and gold analysis. Par exemple, a 10% jump in oil prices can push gold prices up by 2–3% because of higher production costs and inflation. In India, studies reveal that the consumer price index and stock market index are the main long-term drivers of gold prices, while exchange rates matter more in the short term. These findings highlight how the gold industry and gold analysis depend on a wide range of economic factors.
Trade and Policy Impacts
Trade policies and tariffs can quickly change the gold industry and gold analysis. When countries add tariffs, costs go up and trade wars may start. This creates uncertainty and inflation, which often leads investors to buy gold. The following points show how trade and policy changes have affected gold prices:
Tariffs raise import costs and can spark trade wars, causing economic uncertainty.
Economic disruptions from tariffs lead to inflation and supply chain problems, increasing demand for gold.
During the US-China trade war (2018–2020), gold prices surged from about $1,200 to over $2,000 per ounce.
Gold acts as a hedge when tariffs make prices unstable.
History shows that trade tensions often push gold prices higher.
Economists use models to study these trends and find that gold prices often rise before economic downturns. Gold’s value as a safe-haven asset becomes clear during times of policy change and market stress.
Industry Performance
The gold industry and gold analysis also depend on how the industry performs compared to other assets. Over the past 50 années, gold has often outperformed stocks, bonds, and other commodities during periods of high inflation and market volatility. The table below shows how gold compares to other investments during economic stress:
Asset Class | Performance During Stress | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Or | Positive returns | Outperforms in high inflation periods |
Equities | Often negative | Sensitive to market downturns |
Bonds | Mixed | Impacted by interest rate changes |
Commodities | Varies | Less stable than gold |
The gold industry and gold analysis reveal that gold remains a reliable choice when economic factors create uncertainty. Investors often turn to gold when other assets lose value, making it a key part of many portfolios.
Interplay of Gold Price Drivers
Recent Market Trends
Recent trends in the current gold market scenario show that many factors work together to shape the price of gold. Investors watch not only inflation and interest rates but also market sentiment and global events. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) reports reveal how investor positions can amplify price movements.
In mid-2020, hedge funds and money managers held a record number of net long positions in gold. This action pushed the price of gold to new highs. When too many investors took the same side, the market became crowded, and a price pullback followed.
In 2021, large speculators shifted to net short positions. This change led to a sharp drop in the price of gold.
Technical factors, such as key price levels like $1,500 ou $2,000, and moving averages, also play a role. These levels often trigger buying or selling, adding to short-term swings.
Fundamental drivers, including inflation, economic crises, and changes in the US dollar, combine with speculative trading to create feedback loops. These loops can make gold prices more volatile.
Investors who track both technical signals and macroeconomic news gain better insight into the direction of gold prices.
Factor Interactions
The price of gold rarely moves because of a single reason. Instead, several factors interact and sometimes amplify each other. Le table below shows how different forces affect gold prices:
Key Factors Influencing Gold Prices | Empirical Findings and Market Trends |
|---|---|
Inflation | Gold often rises when inflation increases, acting as a hedge. |
Exchange Rates | Changes in currency values impact the price of gold. |
Interest Rates | Higher rates usually lower gold’s appeal. |
Economic Growth | Strong growth can boost demand for gold in manufacturing. |
Volatility and Structural Breaks | Sudden changes in the economy can disrupt gold price patterns. |
Market Forces (Stocks, Bonds) | Stock and bond movements often link to gold price changes. |
Global Events | Crises like COVID-19 increase demand for gold as a safe haven. |
Central Bank Policies | Decisions by major banks, such as the Federal Reserve, shape gold prices. |
Geopolitical tensions, such as conflicts or trade wars, often cause investors to seek safety in gold. Par exemple, airstrikes or sanctions can quickly drive up the price of gold. En même temps, economic factors like inflation and interest rates change how attractive gold looks compared to other assets. Central bank actions, currency strength, and even cultural demand all play a part. Market sentiment can shift quickly, making the price of gold move in unexpected ways.
Gold prices respond to real interest rates, the US dollar, inflation, and global events. Investors who track these factors can make smarter choices. They should review market trends often and adjust their investment portfolio as needed.
Watch central bank actions and supply changes
Stay alert to geopolitical risks
Careful gold analysis helps investors protect their wealth and plan for the future.
FAQ
What makes gold a safe haven during economic uncertainty?
Gold acts as a safe-haven asset because people trust its value during economic uncertainty. When other investments lose value, gold often keeps its worth. Many investors add gold to their investment portfolio to protect against sudden changes in the market.
How do supply and demand affect gold prices?
Supply and demand play a big role in setting gold prices. When demand for gold rises but gold supply stays the same or drops, the price of gold usually goes up. The gold industry and gold analysis track these trends closely.
Why do geopolitical factors impact the price of gold?
Geopolitical factors, like wars or trade disputes, create risk in the current gold market scenario. Investors often buy gold as a store of value when geopolitical and economic uncertainty increases. This extra investment demand can push prices higher.
Does inflation always raise gold prices?
Inflation concerns often lead people to buy gold, but inflation-adjusted prices do not always move the same way. Other key factors influencing gold price, such as market sentiment and economic factors, also matter. Gold investment can help protect against rising prices.
How do central banks influence the value of gold?
Central banks buy and sell gold to manage reserves. Their actions can change the value of gold and affect gold prices worldwide. Central banks often buy gold as a safe haven during times of economic uncertainty.





WhatsApp
Scannez le code QR pour démarrer une discussion WhatsApp avec nous.